The following article comes from Suzhou CDC, and the author is Suzhou CDC.

Suzhou disease control.
Disease control institution
Suzhou CDC WeChat WeChat official account
In the cold winter.
Infectious diseases such as influenza and mycoplasma pneumonia are high.
To this end, Suzhou CDC released
Guidelines for vaccination of respiratory infectious diseases in high incidence period
Let’s watch it together!
?
flu
Influenza is an acute respiratory infectious disease caused by influenza virus, which is highly contagious, mainly spread by droplets, but also indirectly through contact with contaminated hands and daily necessities. People are generally susceptible. After infection, they will gain a certain degree of immunity to the same subtype, but there is no cross-immunity between different subtypes, so people can get sick repeatedly because of different subtypes of infection.
Vaccination of influenza vaccine every year is the most effective means to prevent influenza. Because the composition of influenza vaccine will change due to the different epidemic dominant strains in that year, it is necessary to vaccinate influenza vaccine every year.
According to the types of influenza virus strains, influenza vaccines are currently divided into trivalent and tetravalent.
The strains covered by trivalent influenza vaccine this year are: influenza A H1N1, influenza A H3N2 and influenza B Victoria; The tetravalent influenza vaccine contains more strains of Yamagata influenza virus B than trivalent influenza vaccine.
At present, the influenza vaccine in Suzhou is a non-immunization program vaccine, which is vaccinated by residents voluntarily at their own expense.
Influenza vaccine immunization program:
1. Adult trivalent and tetravalent inactivated influenza virus vaccine, the target of vaccination is people aged 3 years and above, with one dose;
2. Children’s trivalent and tetravalent inactivated influenza virus vaccine, the vaccination target is children aged 6-35 months, and 1 or 2 doses are inoculated according to the vaccine instructions of different manufacturers;
3. Live attenuated trivalent influenza vaccine, targeted at children and adolescents aged 36 months to 17 years, with one dose.
Pneumococcal disease
Streptococcus pneumoniae (Spn) is the main pathogen causing pneumonia, meningitis, bacteremia and other serious diseases in children, and it is also the common cause of acute otitis media and sinusitis.
Pneumococcus is often temporarily colonized in human nasopharynx, and infants are the main hosts, which are generally transmitted by respiratory droplets or caused by colonized bacteria.
WHO lists pneumococcal diseases as diseases requiring "extremely high priority" for vaccine prevention. At present, the pneumococcal vaccines approved for marketing in China are divided into 13-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide conjugate vaccine (PCV13) and 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPV23).
PCV13
At present, there are three kinds of PCV13 listed in China, all of which are suitable for infants and children aged 6-5 (before their 6th birthday). Specific vaccination procedures are as follows:
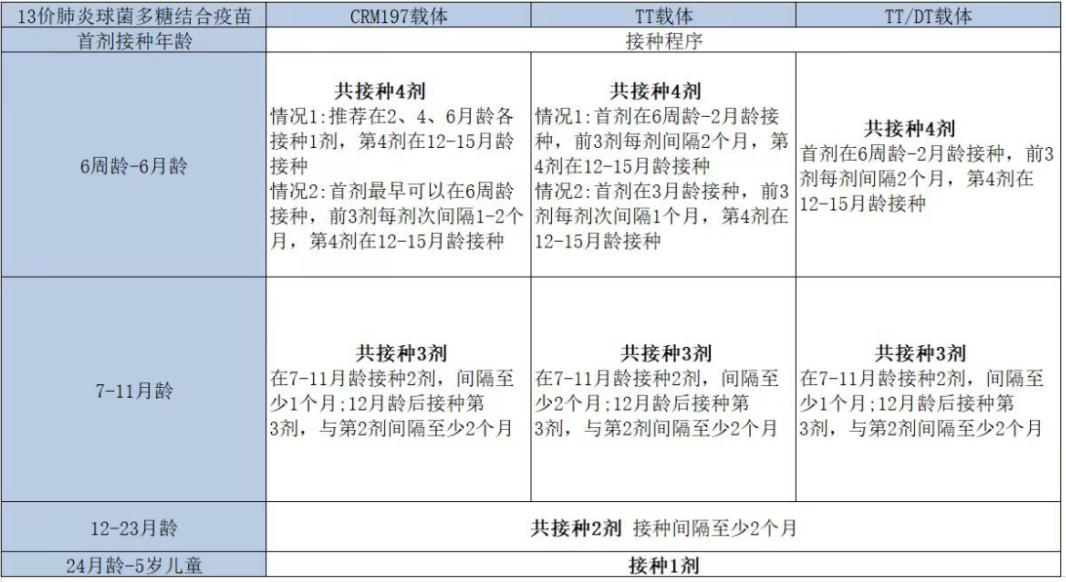
PPV23
PPV23 is used for people over 2 years old with increased risk of pneumococcal infection and pneumococcal diseases, especially but not limited to the following key populations:
① the elderly population;
② Individuals with chronic cardiovascular diseases (including congestive heart failure and cardiomyopathy), chronic lung diseases (including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and emphysema) or diabetes;
③ Individuals suffering from alcoholism, chronic liver diseases (including cirrhosis) and cerebrospinal fluid leakage;
④ Functional or anatomical individuals without spleen;
⑤ People with impaired immune function (including HIV-infected people, leukemia, lymphoma, Hodgkin’s disease, multiple myeloma, common malignant tumors, patients with chronic renal failure or nephrotic syndrome), patients with immunosuppressive therapy (including corticosteroids) and patients with organ or bone marrow transplantation.
Usually, only one dose should be inoculated to the target. For those who need multiple cropping, they should be inoculated according to the instructions, and the interval of multiple cropping should be at least 5 years.
In order to implement the "531" action plan of Suzhou Healthy City, implement major infectious disease prevention and control projects, further reduce the incidence of pneumococcal pneumonia among the elderly in this city, and reduce the disease burden caused by the disease, Suzhou City has implemented free vaccination of 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine for the elderly over 65 years old in the city since April 2018. During the implementation of the project, every eligible elderly person can enjoy a free vaccination.
Mumps, measles and rubella
01
epidemic parotitis
Mumps is an acute respiratory infectious disease caused by mumps virus, which is more common in children and adolescents, but also in adults. It occurs in winter and spring, and it is easy to break out in schools, nurseries, kindergartens and other places where children are concentrated.
02
measles
Measles is caused by measles virus, which is highly contagious, and human beings are generally susceptible to measles virus. Patients are the only source of infection and spread from person to person through respiratory droplets.
03
rubella
Rubella is caused by rubella virus and is highly contagious. Rubella patients are the source of rubella infection and spread through respiratory droplets. Typical rubella has a pink mottled rash, which is easy to distinguish from measles with patchy dark red spots and papules. The mother suffers from rubella during pregnancy, and the virus can invade the fetus through the placenta, which may lead to fetal malformation, premature delivery, abortion and other dangers.
Vaccination with measles vaccine (MMR) is an effective means to prevent the above three infectious diseases.
Suzhou is currently carrying out the work of leak detection and replanting of vaccines containing measles components. Children aged 8-17 months who have not been vaccinated with measles vaccine, and children aged 18 months -18 years who have not been vaccinated with measles vaccine for 2 doses, all children who have no contraindications for vaccination with measles vaccine are the recipients.
In addition, in order to improve the level of protective antibodies against measles and rubella among teenagers, reduce the incidence of measles and rubella among the target population in adulthood, and reduce the risk of neonatal congenital rubella syndrome caused by rubella infection in women’s reproductive stage, Suzhou City has included the enhanced immunization program of measles and rubella vaccine for junior middle school students in local immunization plans, and all junior middle school students who are in good health and have no contraindications to measles and rubella vaccine can receive a dose of measles and rubella vaccine for free.
chickenpox
Chickenpox is a common infectious disease in children caused by varicella-zoster virus infection. Chickenpox patients are the only source of infection, mainly through respiratory droplets and direct contact.
The disease is highly contagious and people are generally susceptible to chickenpox. Persistent immunity can be obtained after illness, and it is rare to get chickenpox again, but herpes zoster can occur repeatedly. This disease can occur all year round, with the peak in winter and spring.
Vaccination program for varicella:
Vaccination with varicella vaccine is the most economical and effective means to control the spread of varicella.
Since January 1, 2023, Jiangsu Province has included live attenuated varicella vaccine in children’s immunization program, and school-age children can receive two doses of live attenuated varicella vaccine free of charge.
Immunization procedures are: the first dose for 12-18 months old, the second dose for 4-year-old children, and the interval between the two doses is not less than 3 months.
epidemic cerebrospinal meningitis
Epidemic cerebrospinal meningitis is purulent meningitis caused by meningococcus, which is a very dangerous acute respiratory infectious disease.
The high incidence season of epidemic cerebrospinal meningitis in China is in winter and spring. Man is the only host of meningococcus, which is spread by droplets or respiratory secretions. Carriers and patients are the main sources of infection. The population is generally susceptible, and the infection rate is the highest among children under 5 years old, especially infants from 6 months to 2 years old.
At present, there are five groups of meningococci causing human diseases: group A, group B, group C, group Y and group W135. The preventable groups of vaccines containing epidemic cerebrospinal meningitis in China are group A, group C, group Y and group W135.
Vaccination program for epidemic cerebrospinal meningitis:
According to the vaccination program of the national expanded immunization program, children aged 6 and 9 months were vaccinated with group A meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine, and A+C meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine was strengthened when they were 3 and 6 years old.
In addition, there are self-funded vaccines containing meningococcal components, including AC conjugate vaccine, AC-b combined vaccine of Haemophilus influenzae (AC-Hib combined vaccine) and ACYW135 group meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine.
Haemophilus influenzae type b
Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib for short) can cause serious diseases in children, such as meningitis, pneumonia, septicemia, cellulitis, pericarditis and osteomyelitis. Hib can be colonized in human nasopharynx, and carriers are the main source of infection, mainly transmitted by droplets. More than 90% of cases of invasive Hib disease occur in children under 5 years old.
Hib immunization program:
In the Hib Vaccine Position Paper published by WHO, since serious Hib diseases mainly occur in children aged 4-18 months, they should be vaccinated as early as 6 weeks after birth.
Hib vaccine is a non-immunization program vaccine, and it is vaccinated according to the principle of voluntary, self-funded and informed consent.
At present, the vaccines containing Hib ingredients approved for marketing in China include: Hib conjugate vaccine, acellular DTP Hib conjugate vaccine (quadruple vaccine), adsorbed acellular DTP inactivated polio and Hib conjugate vaccine (quintuple vaccine), and AC meningococcal (conjugate) Hib conjugate vaccine (meningococcal AC-Hib conjugate vaccine).
(1) Hib conjugate vaccine
(1) Infants under 6 months old: from 2 months old or 3 months old, once every 1 month or 2 months, for 3 times in total. At the age of 18 months, one more booster immunization can be given.
(2) Infants aged 6-12 months: once every 1 month or 2 months, twice in total. At the age of 18 months, one more booster immunization can be given.
(3) Children aged 1-5: Only once.
(2) Quadruple vaccine
Three doses of basic immunization were given at the age of 3, 4 and 5 months; One dose of booster immunization was given at the age of 18-24 months.
(3) Five vaccines
Three doses of basic immunization were given at the age of 2, 3 and 4 months or 3, 4 and 5 months; One dose of booster immunization was given at the age of 18 months.
(4) meningococcal AC-Hib combined vaccine
(1) Vaccination begins at the age of 2-5 months, and a total of 3 doses are required, with an interval of 1 month for each dose;
(2) Vaccination begins at the age of 6-11 months, and a total of 2 doses are required, with an interval of 1 month for each dose;
(3) Vaccination is started at the age of 12-71 months, and only one dose is needed.
December 2023
Adult vaccination outpatient information in Kunshan City
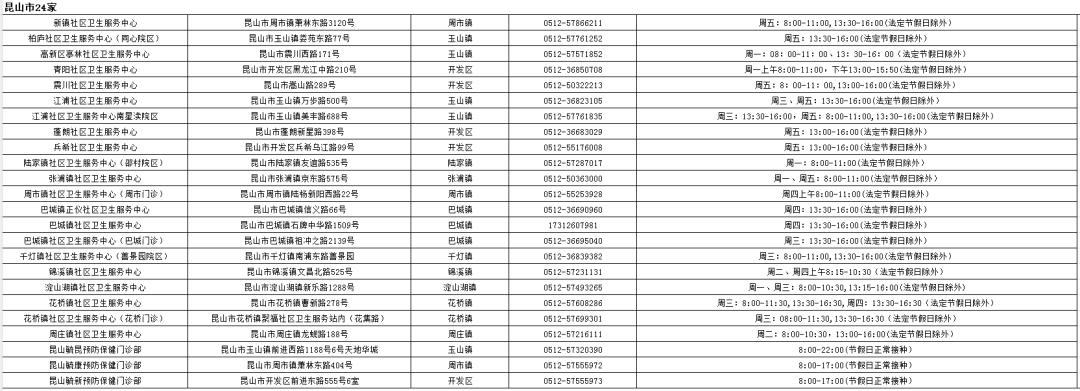
(▲ Click to view a larger image)
December 2023
Outpatient information of children vaccination in Kunshan City
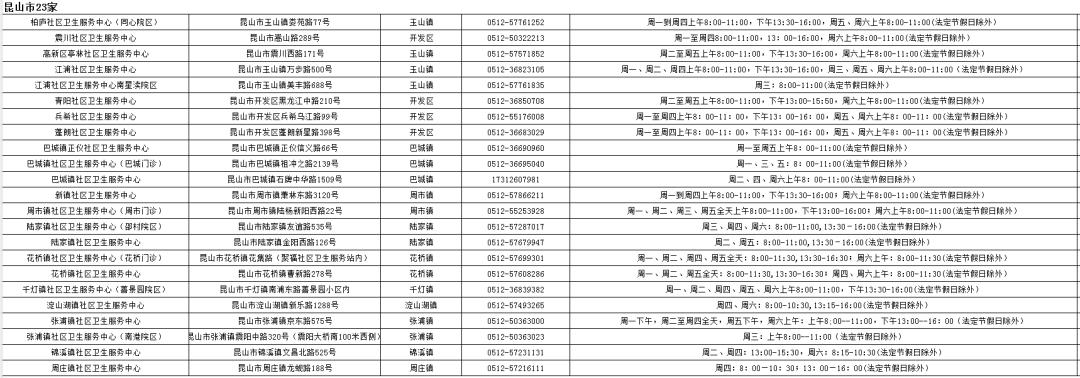
(▲ Click to view a larger image)
·
Original title: "Prevention of respiratory infectious diseases, vaccination guide is coming! 》
Read the original text